Load Balancers: The Complete Guide to Scaling Web Applications
As web applications grow and user traffic increases, ensuring optimal performance and availability becomes crucial. Load balancers are essential components that distribute incoming requests across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about load balancers.
What is a Load Balancer?
A load balancer is a networking device or software application that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple backend servers. Think of it as a traffic director that ensures no single server bears too much demand, improving the overall performance, reliability, and availability of your application.
- • High Availability: If one server fails, traffic is redirected to healthy servers
- • Scalability: Easily add or remove servers based on demand
- • Performance: Distribute load to prevent server overload
- • Flexibility: Route traffic based on various algorithms and rules
Types of Load Balancers
1. Layer 4 (Transport Layer) Load Balancers
Layer 4 load balancers operate at the transport layer and make routing decisions based on IP addresses and port numbers. They don't inspect the actual content of the packets, making them faster but less flexible.
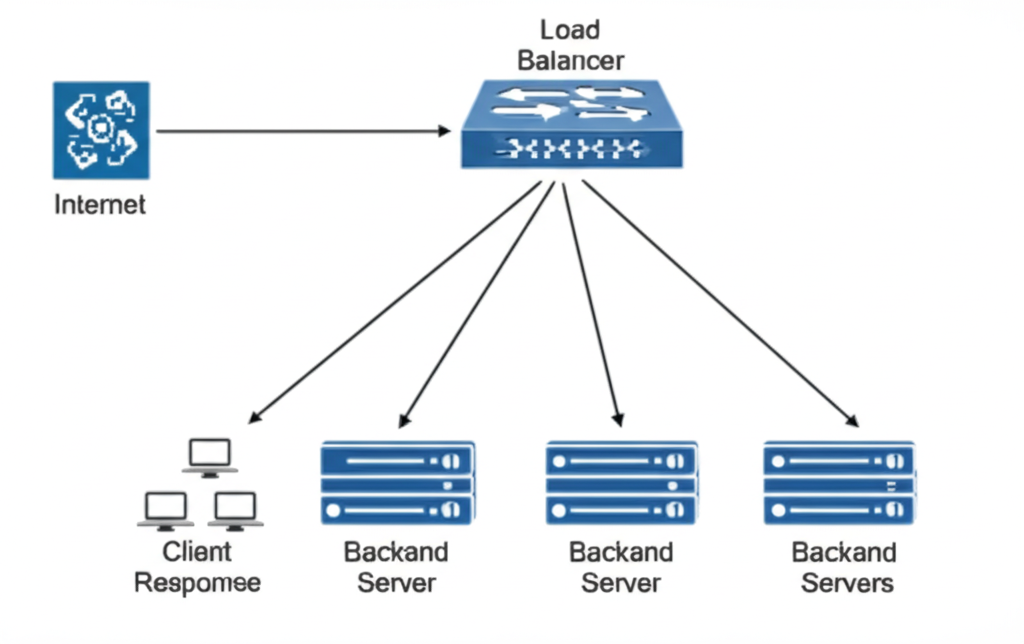
2. Layer 7 (Application Layer) Load Balancers
Layer 7 load balancers operate at the application layer and can make intelligent routing decisions based on the content of the HTTP requests, such as URLs, headers, and cookies. This allows for more sophisticated routing strategies.
Load Balancing Algorithms
Requests are distributed sequentially across all available servers. Simple and effective for servers with similar capabilities.
Similar to round robin but assigns different weights to servers based on their capacity or performance.
Routes traffic to the server with the fewest active connections. Ideal for applications with varying request processing times.
Uses a hash of the client's IP address to determine which server to route to, ensuring session persistence.
Implementation Strategies
Hardware vs Software Load Balancers
Hardware Load Balancers: Dedicated physical devices that offer high performance and reliability but come with higher costs and less flexibility.
Software Load Balancers: Applications that run on standard servers, offering more flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Popular options include Nginx, HAProxy, and cloud-based solutions.
Health Checks and Monitoring
Effective load balancing requires continuous monitoring of server health. Load balancers perform regular health checks to ensure traffic is only routed to healthy servers. Common health check methods include:
- HTTP/HTTPS status checks
- TCP connection tests
- Custom application-specific health endpoints
- Response time monitoring
Best Practices
- • Plan for Redundancy: Implement multiple load balancers to avoid single points of failure
- • Monitor Performance: Continuously track metrics like response times, error rates, and server utilization
- • Configure Proper Timeouts: Set appropriate connection and request timeouts to handle slow servers
- • Implement SSL Termination: Offload SSL processing to the load balancer for better performance
- • Use Session Persistence Wisely: Balance between user experience and load distribution
Conclusion
Load balancers are fundamental components of modern web architecture, enabling applications to scale efficiently and maintain high availability. By understanding the different types, algorithms, and implementation strategies, you can make informed decisions about the best load balancing solution for your specific needs.
Whether you're building a small web application or a large-scale distributed system, proper load balancing will help ensure your users have a fast, reliable experience while giving you the flexibility to scale as your business grows.